Okay, I understand. Here's an article exploring Coinbase's profit model and revenue streams, aiming for a detailed and insightful explanation without using bullet points or numbered lists.
Coinbase, a behemoth in the cryptocurrency exchange world, has become synonymous with onboarding new users into the digital asset ecosystem. But how does this platform, facilitating billions of dollars in trades, generate its revenue and ultimately, profit? Understanding Coinbase's business model requires delving into its diverse revenue streams and dissecting the strategic decisions that underpin its profitability.
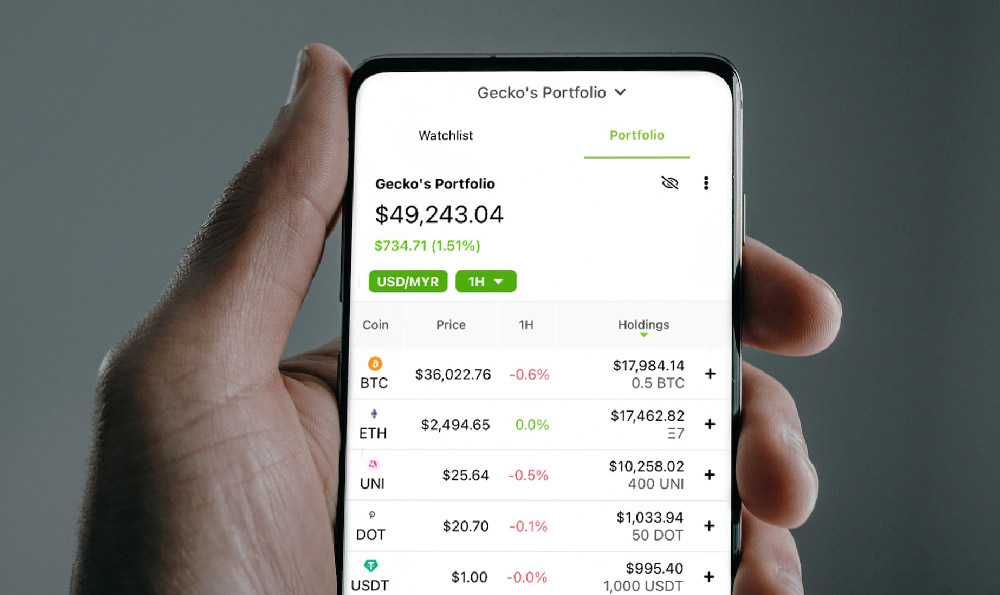
The most significant contributor to Coinbase's revenue is undeniably transaction fees. Whenever a user buys or sells cryptocurrency on the platform, Coinbase charges a fee based on the transaction value. The specifics of this fee structure are complex, varying based on factors like the user's trading volume, the type of account they hold (Coinbase vs. Coinbase Pro), and the payment method used. Generally, users on the basic Coinbase platform face higher, simpler fees designed for ease of use, while Coinbase Pro users benefit from a tiered fee structure that incentivizes higher trading volumes with lower rates. These transaction fees are the lifeblood of Coinbase, fluctuating directly with the volume of cryptocurrency trading activity. During periods of market volatility and heightened interest, Coinbase sees a surge in trading volume, translating directly to increased revenue. Conversely, during market downturns or periods of low volatility, transaction revenue can decline significantly, highlighting the reliance of Coinbase's core profitability on the overall health and activity of the crypto market.

Beyond simple buy/sell transactions, Coinbase generates revenue through a suite of services designed to cater to both retail and institutional investors. One notable avenue is Coinbase Prime, a comprehensive platform tailored to the needs of institutional clients, including hedge funds, asset managers, and corporations. Coinbase Prime offers advanced trading tools, secure custody solutions, and access to liquidity pools, all bundled with a higher fee structure that reflects the premium services provided. This institutional-focused approach is crucial for diversifying Coinbase's revenue streams and mitigating its reliance solely on retail trading volume. Large institutions engaging in high-volume trading contribute significantly to the overall revenue base, and Coinbase Prime is designed to attract and retain these valuable clients.
Coinbase also generates revenue from its custody services, providing secure storage solutions for cryptocurrencies. Custody is a critical service, especially for institutional investors holding large sums of digital assets, as it addresses the security concerns associated with self-custody. Coinbase Custody offers both cold storage (offline) and warm storage (online) options, each with varying levels of security and accessibility. The fees charged for custody are typically based on the value of assets stored, providing a recurring revenue stream that is relatively stable compared to the fluctuations of transaction fees. As more institutions enter the crypto space and require robust custody solutions, this revenue stream is expected to grow in importance.
Furthermore, Coinbase offers staking services, allowing users to earn rewards for participating in the validation of certain blockchain networks. By staking their cryptocurrency holdings through Coinbase, users contribute to the security and efficiency of the network and, in return, receive staking rewards. Coinbase takes a commission on these rewards, generating revenue while providing a valuable service to its users. The popularity of staking is growing as more proof-of-stake blockchains emerge, making this a promising area for future revenue growth.
In addition to these core revenue streams, Coinbase is actively diversifying its offerings to include subscription-based services and data analytics products. Coinbase One, a subscription service, offers users zero trading fees and enhanced customer support for a monthly fee. This model aims to create a more predictable and recurring revenue stream, fostering customer loyalty and providing a consistent source of income even during periods of market downturn. Moreover, Coinbase leverages its vast data resources to develop analytics products and market insights, which are sold to institutional clients and businesses interested in understanding cryptocurrency market trends. This data-driven approach provides a valuable service to market participants and generates an additional revenue stream for Coinbase.
Finally, Coinbase occasionally benefits from interest income generated on its cryptocurrency holdings and fiat currency reserves. While not a primary revenue driver, this income contributes to the overall profitability of the company. The amount of interest income generated depends on prevailing interest rates and the size of Coinbase's reserves, fluctuating with market conditions and the company's financial strategies.
In conclusion, Coinbase's profitability hinges on a multifaceted approach that leverages transaction fees, institutional services, custody solutions, staking rewards, subscription models, data analytics, and interest income. While transaction fees currently represent the lion's share of revenue, Coinbase is actively pursuing diversification strategies to mitigate its dependence on market volatility and ensure long-term sustainability. By expanding its offerings and catering to both retail and institutional investors, Coinbase is positioning itself to remain a dominant player in the ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape. The success of Coinbase's future profitability will largely depend on its ability to continue innovating, attracting new users, and navigating the regulatory challenges that inevitably accompany the growth of the crypto industry.